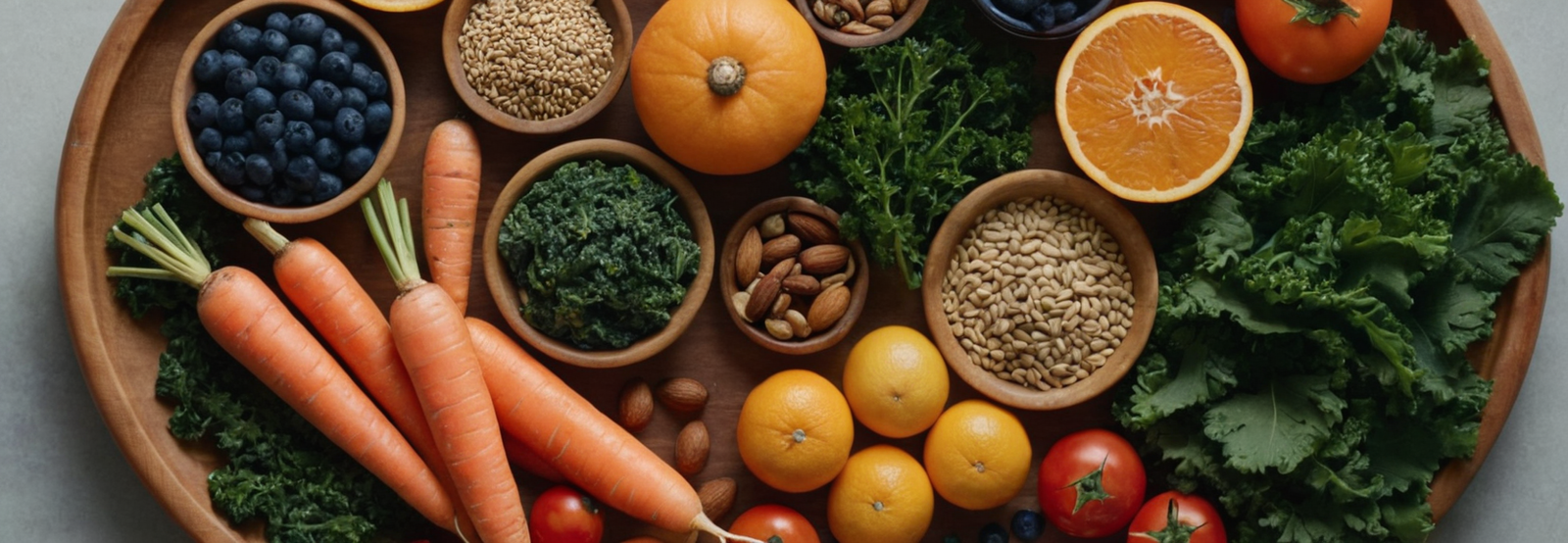
You live in a hurry. Meetings, long screen time, deadlines. But your health counts more than the next notification or task. Choosing vitamin-rich food gives you all your body needs. Nutrition supplements look convenient, but they fall short in structure, safety, and science.
In the high-stress, always-online world, real food vitamins help your brain, energy, and resilience. Start with small steps. Build habits. Use knowledge. This article shows why food wins and how you fit it into your work life.
Why real-food vitamins outperform supplements
Food brings positive complexity
Whole foods deliver vitamins plus cofactors, fiber, antioxidants, and structure that help absorption and support your cells. Supplements strip vitamins from necessary context.
Supplements show no longevity benefit and may even backfire
A major analysis of nearly 400,000 healthy adults tracked over 20+ years found no reduction in mortality for those taking daily multivitamins – and even a 4 percent higher mortality risk compared to non-users.1 2 The study saw no significant differences for death from heart disease, cancer, or stroke.3
Poor regulation, inconsistent quality
Supplements don’t have to prove safety or efficacy before arriving on shelves. In the USA, the FDA only steps in after they cause harm. Ingredients vary, and ‘proprietary blends’ can mask dosages or include undisclosed additives.4
Limited benefit for healthy people
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2022 found little to no evidence that vitamins prevent chronic disease or death in properly nourished adults.5
Sourced from 6
Supplements and prescribed vitamins have specific uses
While most healthy adults can meet their vitamin needs through real food, certain supplements are valid in specific situations. For example, folic acid is recommended for women planning pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects, and vitamin B12 supplements are advised for older adults or individuals on strict vegan diets who may struggle to absorb enough from food.
Some nutrients are provided as medicaments prescribed by a doctor rather than over-the-counter pills chosen without proper consultation. For instance, patients with diagnosed vitamin D deficiency may receive high-dose prescription vitamin D to restore optimal levels safely. These targeted interventions differ from general multivitamins and should always follow professional medical guidance.
Vitamin-rich foods you can eat today
Delivering nutritions should mainly come from food. Choose foods that deliver multiple vitamins per bite. Table below helps you to chose wisely and is a snapshot to show how much of a vitamins we may get from regular food.
| Vitamin | Food examples | Role in your body |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Carrots, sweet potatoes, kale, liver | Vision, immune response, skin repair, cell growth |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | Whole grains, pork, legumes, sunflower seeds | Energy metabolism, nerve function |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Milk, eggs, spinach, almonds | Energy release, red blood cell production, skin health |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Chicken, turkey, tuna, peanuts | Converts food into energy, supports nervous system |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | Avocados, mushrooms, chicken, whole grains | Hormone production, energy metabolism |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | Chickpeas, bananas, salmon, potatoes | Neurotransmitter production, hemoglobin creation |
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | Eggs, nuts, seeds, salmon | Hair, skin, nail health, metabolism of fats and proteins |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | Spinach, kale, lentils, black beans | DNA synthesis, cell growth, pregnancy health |
| Vitamin B12 | Fish, shellfish, eggs, dairy, fortified cereals | Red blood cell production, nerve function, DNA synthesis |
| Vitamin C | Oranges, strawberries, kiwis, kale, bell peppers | Immune support, collagen production, antioxidant |
| Vitamin D | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified dairy, sun exposure | Bone strength, immune system, mood regulation |
| Vitamin E | Sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, hazelnuts | Antioxidant protection, immune function, skin health |
| Vitamin K1 | Kale, spinach, Brussels sprouts, broccoli | Blood clotting, bone health, brain function |
| Vitamin K2 | Fermented foods (e.g. sauerkraut), hard cheeses, egg yolks | Bone mineralization, cardiovascular protection |
Connect vitamins with your digital lifestyle
In the digital world, you’re focused on tasks and attached to screens. Long hours, blue light, fast food or cereal in between meetings drain your body. Real-food vitamins power your brain, support energy, stabilize mood, and safeguard focus.
How superfood helps with regeneration for digitally active people?
Your corporate world responds better to small, consistent changes than drastic diets or expensive pills.
Start small. Build lasting habits
One way to start is to follow these tips to upgrade your nutrition without adding stress:
- Morning green power: Add a handful of raw kale or spinach to your breakfast smoothie or omelet,
- Smart snacking: Choose an orange, kiwi, or berries instead of processed bars,
- Balanced lunch: Include legumes or whole grains and add a leafy-green side,
- Fat-powered absorption: Eat vitamins with healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, nuts to boost uptake of fat-soluble vitamins,
- Consistent greens: Keep vitamin-K intake stable – especially important if you’re on medication like blood thinners.7
Healthy foods contain more than the one specific vitamin or mineral found in supplements. They simply can’t replicate the wide array of benefits and nutrients.
Janice Hermann
Once you notice improved focus, reduced fatigue, better immunity, you’ll want more of that real-food impact.
Sources
- NIH, “For healthy adults, taking multivitamins daily is not associated with a lower risk of death” ↩︎
- The Guardian, “Daily multivitamins do not help people live longer, major study finds” ↩︎
- JPC, “Long-Term Study Finds No Mortality Benefit in Daily Multivitamin Use for Adults 20+” ↩︎
- Verywellhealth, “Verywell Health’s Dietary Supplement Methodology” ↩︎
- Nypost, “Millions of Americans take multivitamins to prevent disease — but here’s why they shouldn’t” ↩︎
- Enterpriseappstoday, “Vitamin and Supplement Industry Statistics By Consumer, Type, Demographic, Country, Distributing Channels, Companies” ↩︎
- Eatingwell, “Can You Eat Kale If You Take Blood Thinners or Aspirin? Here’s What Health Experts Say” ↩︎